Technology often helps us to carry out tasks in a more agile and simple way and, as is the case with electronic signatures, to break the distance barrier. Despite its advantages, and due to the lack of knowledge about this tool, there are still many users who question its security.
In this post we have compiled some of the key aspects that you should know about the security of electronic signatures and the reasons why it is so difficult to forge them.
How secure is the electronic signature?
An electronic signature is a tool used by a person to accept and validate the content of any electronic documentation or transaction.
The eIDAS Regulation includes three types of electronic signature, each of which is associated with a different level of security and the generation of proof and evidence:
- Simple electronic signature: this is the most basic signature. It lacks certainty as to the content of the document and it is impossible to associate the signature with the signatory. An example of this type of signature could be when entering the PIN code to make a payment with a bank card.
- Advanced electronic signature: this is based on a process that makes it possible to univocally identify the holder and to detect any subsequent changes to the signed data. They can be based on a digital certificate or not.
- Qualified electronic signature: provides the highest level of security and maximum legal guarantees, avoiding situations of vulnerability. In this type of signature, in addition to other requirements, it is essential that a digital certificate is used.
As we have just seen, not all electronic signatures offer maximum security against possible threats of forgery or misuse. In the following section we will see how those signatures based on a digital certificate have a high degree of reliability.
Why is it so difficult to forge an electronic signature based on a digital certificate?
The electronic signature with a digital certificate uses a cryptographic mechanism that makes it practically impossible to forge. Its operation is based on the use of public and private keys generated by an algorithm:
- The public key will be known among the parties involved in the process and allows access to the document.
- The private key is given only to the certificate holder - the signatory - and is known only to him.
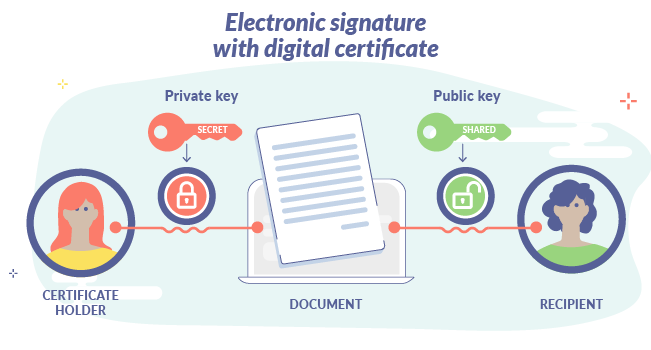
The procedure of signature creation using a digital certificate is as follows:
1. An algorithm generates a private key together with its corresponding public key.
2. Another creates the signature by receiving the private key as well as the document or message to be signed, which is encrypted by the private key itself.
3. A third algorithm verifies the authenticity of the signed document or message with the public key associated with the private key.
With this encryption system, if the certificate holder's private key is not known, it is practically impossible to forge the signature.
In the case of Uanataca's digital certificates, if for any reason the holder suspects that their digital certificate may have been compromised, they can suspend or revoke it quickly and easily via the Uanataca website. The advantage of suspending the certificate is that the holder can reactivate it at any time.
5 key aspects that give the electronic signature with digital certificate maximum security and legal guarantees
1.- Encryption system
As mentioned in the previous section, thanks to encryption technology, the data in the document is made intelligible to unauthorised persons, at the same time allowing the signature to achieve maximum levels of security such as authentication, integrity and non-repudiation, the latter in the case of qualified electronic signatures.
2.- Qualified digital certificate
There are two types of digital certificate: qualified, i.e. issued by a Qualified Trust Service Provider, and unqualified.
The "Qualification" of a digital certificate provides additional guarantees for several reasons. One of them is compliance with the stipulations of the eIDAS Regulation regarding the information contained in the certificate. This guarantees the veracity of its data, its origin and ensures the content verification process.
Another guarantee is provided by the figure of the issuer, which we will expand on in more detail in the following point.
3.- Provider guarantees
Qualified digital certificates can only be issued by a Qualified Trust Service Provider such as Uanataca. This figure reliably guarantees the identity of the natural or legal person to whom a qualified certificate is issued.

In addition, PCSCs are subject to a number of requirements that guarantee the security of their trusted electronic services: qualified personnel, reliable systems and products that are protected and adequate measures against falsification and data theft.
4.- Non-repudiation
The qualified electronic signature is based on a digital certificate. It is known because it provides a presumption of veracity and therefore non-repudiation of the signature. In addition, it provides the highest level of security and maximum legal guarantees, avoiding situations of vulnerability.
Beyond the forgery of the signature, which we have already mentioned is almost improbable if it is carried out with a digital certificate, we must be concerned that the signatory does not repudiate the signature. Non-repudiation represents an extra security that prevents the signatory from not recognising his signature and renouncing his obligations.
5.- Signature validation
Electronic signature validation adds another layer of security to the signature process by validating the signature once it has been made.
This mechanism allows the recipient of a digitally signed document to identify the issuer of the document, confirm that the document has not been altered since it was signed, and be certain of the signatory's exclusive control over the use of the electronic signature creation data.
Uanataca's signature validation service is fast, reliable and allows you to validate large quantities of documents in an automated way.
In conclusion, the forgery of an electronic signature is very complicated if a mechanism as secure as a digital certificate is used. Moreover, if the certificate is issued by a Qualified Trust Service Provider, we ensure a series of additional guarantees that protect us against risk situations.